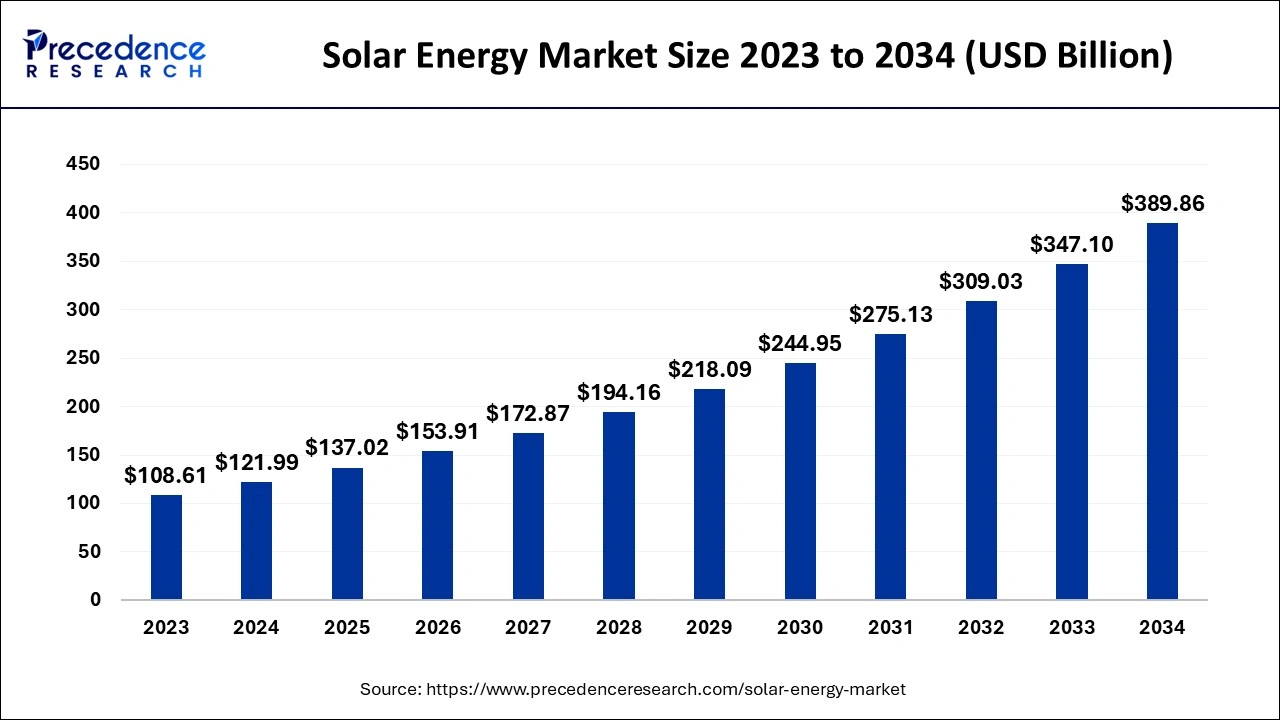
The global solar energy market size reached USD 121.99 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 389.86 billion by 2034, growing at a remarkable CAGR of 12.32% from 2024 to 2034.
The solar energy market has been experiencing rapid growth, driven by increasing demand for renewable energy sources and global efforts to reduce carbon emissions. Solar energy, harnessed through photovoltaic (PV) systems and concentrating solar power (CSP), is becoming one of the most viable solutions to address environmental concerns and energy security. As the cost of solar panels continues to fall, and technological advancements improve energy efficiency and storage capabilities, the adoption of solar energy is growing across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. Governments worldwide are also incentivizing solar adoption through subsidies, tax credits, and favorable policies, further boosting the market.
The growth of the solar energy market is expected to continue as solar power becomes more integrated into national grids and decentralized power generation systems. Emerging economies with abundant sunlight, combined with increasing energy needs, present significant opportunities for solar energy deployment. Additionally, innovations such as solar storage solutions, floating solar panels, and building-integrated photovoltaics are opening up new possibilities in the market.
Get a Sample: https://www.precedenceresearch.com/
Table of Contents
ToggleSolar Energy Market Trends
- Residential Solar Market Challenges: The U.S. residential solar market is facing contraction, with a notable 25% decline in installed capacity year-over-year in Q1 2024. This downturn is attributed to high interest rates, the transition to net billing tariffs in California, and rising customer acquisition costs.
- While some states are still experiencing growth, the national market is expected to shrink by around 14% in 2024
- Solar-plus-Storage Growth: There is an increasing adoption of solar-plus-storage systems, particularly in commercial and residential sectors. This growth is driven by rising demand for energy independence and resilience, especially in areas prone to power outages.
- Commercial Solar Expansion: The commercial solar market is expected to grow by 14% in 2024, with California and Illinois driving the increase. However, the market still faces challenges, including high financing costs and project development delays.
- Utility-Scale Solar Slowing Down: Utility-scale solar projects are experiencing slower growth due to labor shortages, supply chain constraints, and trade policy uncertainties. Although the project pipeline remains strong, these factors are suppressing immediate growth.
- Impact of the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA): The full impact of the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act is starting to be realized, with incentives for solar manufacturing and installation, especially in the residential and commercial segments. This has led to more domestic production and investment in the solar sector.
- Increased Focus on Solar Manufacturing: The solar manufacturing sector is facing pressure due to rising material costs and the need for technological advancements. However, the IRA’s incentives are expected to help strengthen domestic solar manufacturing capabilities.
- Technological Innovation: Advancements in solar panel efficiency, such as bifacial modules and tracker systems, are becoming more widespread. These innovations improve energy output and decrease the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) from solar projects.
Asia Pacific dominated the global solar energy market with 36% of market share in 2023
Asia Pacific is the dominant region in the global solar energy market, driven by a combination of favorable geographic conditions, strong government policies, increasing demand for renewable energy, technological advancements, and substantial investments. This dominance is expected to continue, with the Asia Pacific solar energy market projected to grow from USD 43.92 billion in 2024 to approximately USD 142.3 billion by 2034, at a CAGR of 12.46%.
Government Support and Policies
Governments in the Asia Pacific region have introduced strong policies to support the adoption and expansion of solar energy. These policies include financial incentives such as subsidies, tax breaks, and feed-in tariffs, which have greatly contributed to the growth of the solar energy sector.
- China: The largest contributor to the region’s market, China aims to reach 1,200 GW of solar capacity by 2030, a massive increase from its current installed capacity. The country has aggressively expanded solar energy installations, becoming a global leader in both manufacturing and capacity.
- India: India’s government has set ambitious renewable energy targets, including a goal of 500 GW of non-fossil fuel-based energy capacity by 2030, which will include solar energy. In addition to this, India has also committed to installing 100 GW of solar capacity, with the government incentivizing solar projects through subsidies and financial schemes.
- Japan: Japan continues to invest in solar energy, leveraging its Feed-in Tariff (FiT) program to encourage solar power generation. The country is also focusing on improving its solar infrastructure, contributing significantly to the regional growth.
Favorable Geography and Climate
Asia Pacific has some of the most favorable geographical conditions for solar energy generation, with many countries enjoying high solar radiation levels and long hours of sunshine. This geographical advantage makes the region highly suitable for large-scale solar energy projects.
- India: With an average of 5-7 hours of sunlight per day in most regions, India is one of the best locations for solar installations. The country’s vast land area further provides opportunities for large solar farms.
- Australia: Known for its high levels of solar radiation, Australia is ideally suited for both residential and commercial solar power projects. The Australian government has also supported this through rebates and incentives for both private and public sector solar installations.
Market Demand and Energy Security
As industrialization, urbanization, and energy consumption continue to rise in the region, the demand for renewable energy, particularly solar power, is also increasing. This demand is partly driven by concerns over energy security and the region’s need to reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
- Energy Security: Countries like Japan, following the Fukushima disaster, have turned to solar power to reduce reliance on nuclear energy. Similarly, China and India are diversifying their energy portfolios to ensure long-term sustainability and energy independence.
Technological Advancements and Cost Reduction
Technological improvements in solar panel efficiency and manufacturing processes have helped reduce the cost of solar installations, making solar energy more accessible.
- China continues to lead in solar panel production, accounting for over 70% of global manufacturing. These advancements have led to a significant reduction in the cost of solar energy installations, further promoting adoption in both residential and commercial sectors across Asia Pacific.
Investment and Financing
The Asia Pacific region has seen substantial investment in solar energy, with both government and private sector funding driving the development of solar infrastructure.
- China and India have attracted billions of dollars in investments from international investors and financial institutions, enabling them to scale up their solar energy projects.
Key Factors Driving the Growth in Asia Pacific Solar Energy Market:
| Factor | Description | Supporting Data |
|---|---|---|
| Government Policies | Strong governmental backing through incentives, feed-in tariffs, and renewable energy targets. | China’s 1,200 GW solar capacity target by 2030 |
| Geography and Sunlight | High levels of sunlight and favorable geographical conditions. | India has an average of 5-7 hours of sunlight/day |
| Market Demand | Increased demand for energy due to industrial growth, urbanization, and energy security concerns. | India’s target of 100 GW solar capacity by 2022 |
| Technological Advancements | Cost reduction in solar panel manufacturing due to technological improvements and economies of scale. | China produces 70% of global solar panels |
| Investment in Infrastructure | Large-scale investments from domestic and international stakeholders. | China and India attract billions in solar investments |
| Market Size (2024-2034) | The Asia Pacific solar energy market is growing rapidly, with significant market size expansion. | Market size projected at USD 43.92 billion in 2024, reaching USD 142.3 billion by 2034 |
Read Also: Hydrogen Market Size to Surpass USD 556.56 Billion by 2034
Case Study: Expansion of Solar Energy in India – 2022-2024
Key Milestones:
- Expansion of Capacity (2022-2024): In 2022, the Pavagada Solar Park, already one of the world’s largest, announced an additional 1,500 MW capacity. By 2024, this park achieved full development, bringing its total capacity to 2,050 MW, making it a model for India’s solar sector growth.
- Government Support and Policy Implementation: The Indian government introduced various incentives, such as the Performance-Based Incentive Scheme, to attract investments. By 2023, over $10 billion in foreign direct investments (FDI) flowed into the solar sector.
- Private Sector Contribution: Key private players, such as Adani Green Energy and ReNew Power, increased their footprint in India’s solar market by securing long-term contracts and developing massive utility-scale solar projects. These projects were critical in achieving India’s renewable energy goals.
Challenges:
- Land Acquisition Issues: In some regions, acquiring land for large-scale solar parks proved to be challenging due to bureaucratic delays and local resistance.
- Supply Chain Constraints: The solar sector faced supply chain disruptions, particularly in importing solar modules due to trade barriers and raw material shortages globally.
Results:
- Increased Solar Capacity: India’s total solar energy capacity reached approximately 50 GW by the end of 2024, marking a significant leap toward achieving the 2030 renewable energy targets.
- Job Creation: The sector generated thousands of jobs, contributing to the overall growth in India’s green economy.
- Cost Reduction: The cost of solar energy per MW dropped by around 20% from 2022 to 2024 due to technological advancements and economies of scale, making solar energy more competitive.
Solar Energy Market Companies
- Canadian Solar
- SolarEdge Technologies
- SunPower Corporation
- First Solar, Inc.
- Enphase Energy, Inc.
- Hanwha Q Cells Co., Ltd.
- Yingli Green Energy Holding Company Limited
- JinkoSolar Holding Co., Ltd.
- Trina Solar
- JA Solar Holdings Co. Ltd.
- Waaree Energies
Recent Developments
- In October 2024, India, GEAPP, and the Uttar Pradesh Expressways Industrial Development Authority announced an INR 1,800 crore solar park project, aiming to establish a 450-500 MW solar power capacity along the Bundelkhand Expressway.
- In October 2024, Ambrane launched its Solar 10K power bank featuring a 10,000 mAh battery and four-fold solar panels, supporting fast charging and sustainability for outdoor enthusiasts.
- In October 2024, Sri Lanka, DH Ceylon Energy introduced a 110 MW Project Apollo solar park in Hambantota, investing USD 82 million to enhance the country’s renewable energy landscape and reduce carbon emissions.
- In September 2024, Gautam Solar announced an INR 1,000 crore investment in a 2 GW solar cell manufacturing facility to meet the growing demand for domestically produced components and support India’s renewable energy targets.